Pre-processing
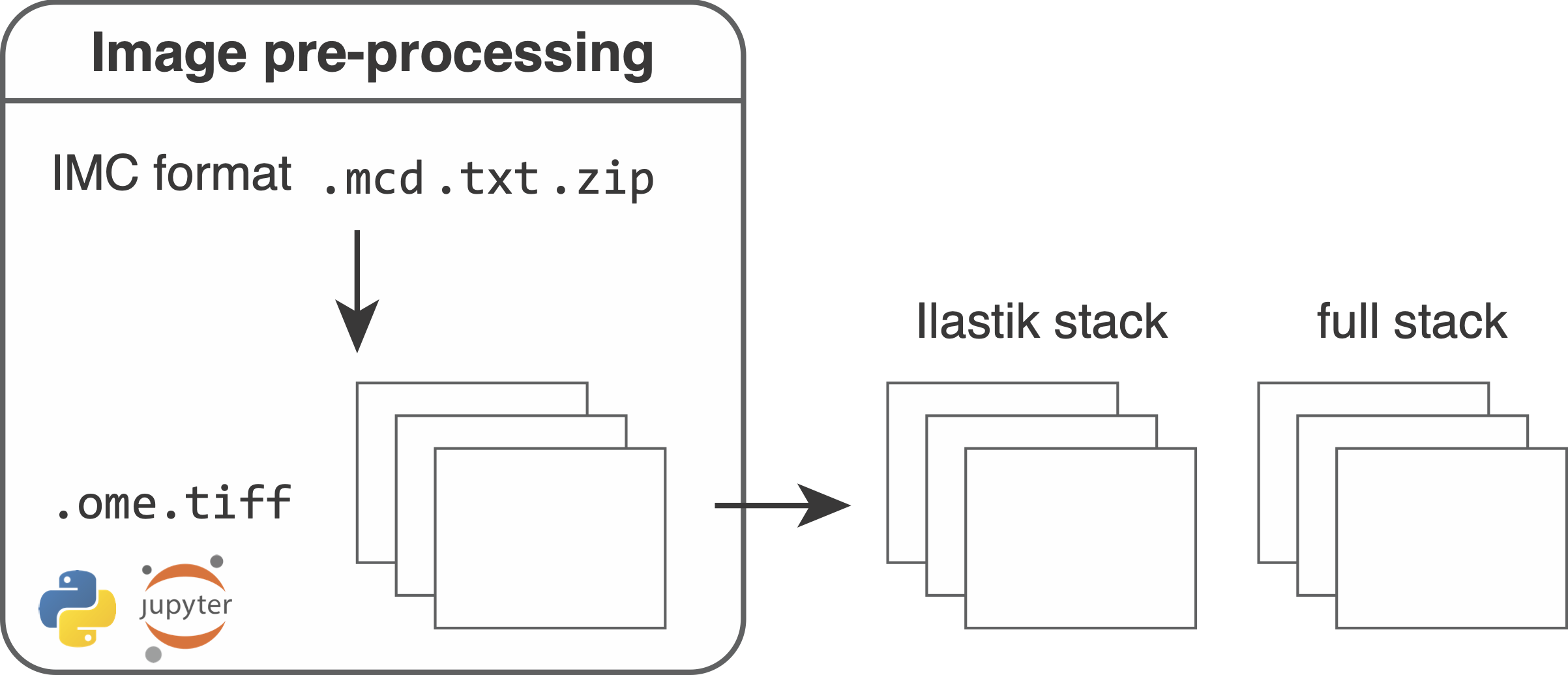
During the first step of the segmentation pipeline, raw data need to be converted to file formats that can be read-in by external software (Fiji, R, python, histoCAT).
Please follow the preprocessing.ipynb script to pre-process the raw data.
To get started, please refer to the instructions here.
Input
The zipped .mcd files
The Hyperion Imaging System produces vendor controlled .mcd and .txt files in the following folder structure:
├── {XYZ}_ROI_001_1.txt
├── {XYZ}_ROI_002_2.txt
├── {XYZ}_ROI_003_3.txt
├── {XYZ}.mcd
where XYZ defines the filename, ROI_001, ROI_002, ROI_003 are names (description) for the selected regions of interest (ROI) and 1, 2, 3 indicate the acquistion identifiers.
The ROI description entry can be specified in the Fluidigm software when selecting ROIs.
The .mcd file contains the raw imaging data of all acquired ROIs while each .txt file contains data of a single ROI.
To enforce a consistent naming scheme and to bundle all metadata, we recommend to zip the folder and specify the location of all .zip files for preprocessing. Each .zip file should only contain data from a single .mcd file and the name of the .zip file should match the name of the .mcd file.
The panel file
The panel file (in .csv format) specifies the type of antibodies that were used in the experiment and all additional channels (e.g. metals used for counterstaining1) that you want to include in downstream processing.
Example entries to the panel file can look like this:
| Metal Tag | Target | full | ilastik |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dy161 | Ecad | 1 | 1 |
| Dy162 | CD45 | 1 | 0 |
| Er166 | CD3 | 1 | 1 |
| Ru100 | Counterstain | 1 | 0 |
Usually there are more columns but the important ones in this case are Metal Tag, full and ilastik.
The 1 in the full column specifies channels that should be written out to an image stack that will be later on used to extract features (also refered to as "full stack").
Here, please specify all channels as 1 that you want to have included in the analysis.
The 1 in the ilastik column indicates channels that will be used for Ilastik pixel classification therefore being used for image segmentation (also refered to as "Ilastik stack").
During the pre-processing steps, you will need to specify the name of the panel column that contains the metal isotopes, the name of the column that contains the 1 or 0 entries for the channels to be analysed and the name of the column that indicates the channels used for Ilastik training as seen above.
Naming conventions
When going through the preprocessing script, you will notice the specification of the _full and _ilastik suffix indicating the two image stacks mentioned above.
Example data
We provide raw IMC example data at zenodo.org/record/5949116. This dataset contains 4 .zip archives each of which holds one .mcd and multiple .txt files. The data was acquired as part of the Integrated iMMUnoprofiling of large adaptive CANcer patient cohorts (IMMUcan) project immucan.eu using the Hyperion imaging system. Data of 4 patients with different cancer types are provided. To download the raw data together with the panel file, sample metadata and a pre-trained Ilastik classifier, please follow the download script.
Conversion fom .mcd to .ome.tiff files
In the first step of the pipeline, raw .mcd files are converted into .ome.tiff files2.
This serves the purpose to allow vendor independent downstream analysis and visualization of the images.
For in-depth information of the .ome.tiff file format see here.
Each .mcd file can contain multiple acquisitions. This means that multiple multi-channel .ome.tiff files per .mcd file are produced.
The Fluor and Name entries of each channel are set.
Here Name contains the actual name of the antibody as defined in the panel file and Fluor contains the metal tag of the antibody.
For IMC data, the metal tag is defined as: (IsotopeShortname)(Mass), e.g. Ir191 for Iridium
isotope 191.
To perform this conversion, we use the extract_mcd_file function of the internal imcsegpipe python package.
It uses the readimc python package to read .mcd files and the xtiff python package to write the .ome.tiff files.
The ometiff output folder for each sample has the following form:
├── {XYZ}_s0_a1_ac.ome.tiff
├── {XYZ}_s0_a2_ac.ome.tiff
├── {XYZ}_s0_a3_ac.ome.tiff
├── {XYZ}_s0_a1_ac.ome.csv
├── {XYZ}_s0_a2_ac.ome.csv
├── {XYZ}_s0_a3_ac.ome.csv
├── {XYZ}_s0_p1_pano.png
├── {XYZ}_s0_slide.png
├── {XYZ}_schema.xml
Next to the individual .ome.tiff files (one per acquisition), .csv files are generated that contain the channel name (the metal isotope) and the channel label (the name of the antibody) in the correct channel order.
The _pano.png files contain brighfield panorama acquisitions of the sample where the slide overview is stored as _p1_pano.png. The _schema.xml file contains the internal metadata of the .mcd file in .xml format.
The .mcd to .ome.tiff conversion step additionally generates the analysis/cpinp/acquisition_metadata.csv file that stores per acquisition metadata for later use in CellProfiler.
Conversion from .ome.tiff to single-channel tiffs
In the next pre-processing step, .ome.tiff files are converted to a format that is supported by the histoCAT software3.
To load images into histoCAT, they need to be stored as unsigned 16-bit or unsigned 32-bit single-channel .tiff files.
For each acquisition (each .ome.tiff file), the export_to_histocat converter function exports one folder containing all measured channels as single-channel 32-bit .tiff files.
The naming convention of these .tiff files is Name_Fluor, where Name is the name of the antibody (or the metal if no name is available) and Fluor is the name of the metal isotope.
For full documentation on the histoCAT format, please follow the manual.
Part of a single histoCAT folder will look as follows:
├── 131Xe_Xe131.tiff
├── Beta-2M-1855((2962))Nd148_Nd148.tiff
├── ...
Conversion from .ome.tiff to multi-channel tiffs
For downstream analysis and Ilastik pixel classification, the .ome.tiff files are converted into two multi-channel image stacks in TIFF format:
1. Full stack: The full stack contains all channels specified by the "1" entries in the full column of the panel file. This stack will be later used to measure cell-specific expression features of the selected channels.
2. Ilastik stack: The Ilastik stack contains all channels specified by the "1" entries in the ilastik column of the panel file. This stack will be used to perform the ilastik training to generate cell, cytoplasm and background pixel probabilities (see Ilastik training).
Additional image stacks can be generated by adapting the panel file and specifying the suffix of the file name.
Hot pixel filtering: Each pixel intensity is compared against the maximum intensity of the 3x3 neighboring pixels. If the difference is larger than a specified threshold, the pixel intensity is clipped to the maximum intensity in the 3x3 neighborhood. Setting hpf=None disables hot pixel filtering in this conversion step.
By default the hot pixel filtered full stack is written out to the analysis/cpout/images folder and the hot pixel filtered Ilastik stack is written out to the analysis/ilastik folder.
The analysis/ilastik folder contains files such as:
├── {XYZ}_s0_a1_ac_ilastik.tiff
├── {XYZ}_s0_a1_ac_ilastik.csv
├── ...
The analysis/cpout/images folder contains following files:
├── {XYZ}_s0_a1_ac_full.tiff
├── {XYZ}_s0_a1_ac_full.csv
├── ...
The matching .csv files contain the channel names (metals) in the correct channel order.
Export of acquisition-specific metadata
In the final step of the pre-processing pipeline, a .csv file containing the full stack channel names (metal isotopes) and a .csv file containing the channel names of the images storing pixel probabilities (see Ilastik training) are written out to the analysis/cpinp/ folder.
Output
After image pre-processing the following files have been generated:
analysis/ometiff: contains individual folders (one per sample) of which each contains multiple.ome.tifffiles (one per acquisition).analysis/histocat: contains individual folders (one per acquisition) of which each contains multiple single-channel.tifffiles for upload to histoCAT.analysis/ilastik: contains the ilastik stacks for pixel classification as well as.csvfiles indicating the channel order.analysis/cpout/images: contains the full stacks for analysis as well as.csvfiles indicating the channel order.analysis/cpout/panel.csv: the panel file was copied into the final output folder.analysis/cpinp: containing theacquisition_metadata.csv,full_channelmeta.csv, andprobab_channelmeta_manual.csvfiles containing acquisition and channel metadata
-
Catena R. et al. (2018) Ruthenium counterstaining for imaging mass cytometry. The Journal of Pathology 244(4), pages 479-484. ↩
-
Goldberg I.G. et al. (2005) The open microscopy environment (OME) data model and XML file: open tools for informatics and quantitative analysis in biological imaging. Genome Biology 6(5), R47. ↩
-
Shapiro D. et al. (2017) histoCAT: analysis of cell phenotypes and interactions in multiplex image cytometry data. Nature Methods 14, pages 873–876. ↩